Extended reality headsets are an emerging technology that have many applications in human-robot interaction. For instance, augmented reality (AR) headsets could be used to visually display a robot’s affordable behaviors through a graphical interface and thus show what the robot is capable of doing. While virtual reality (VR) is particularly advantageous when remotely controlling robots, as in teleoperation.
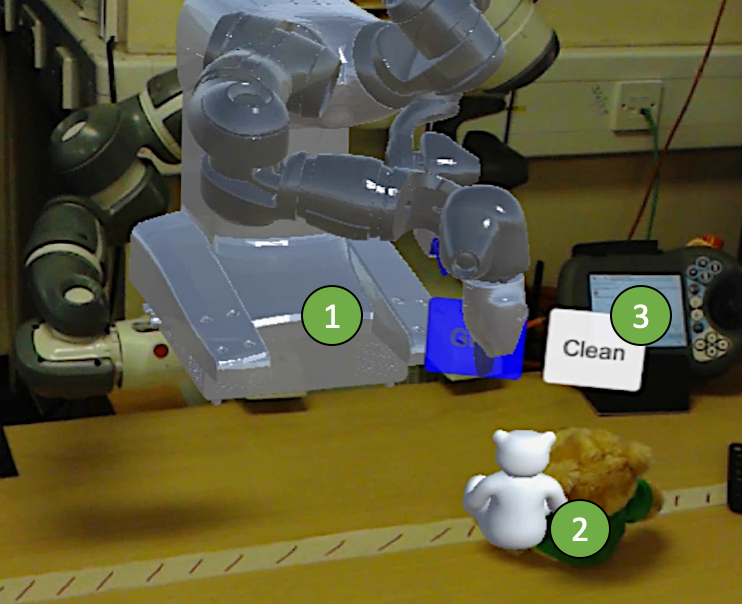
The image on the right (taken from our paper [1]) illustrates how a dual-arm collaborative robot’s affordable behaviors can be visualized by someone wearing an AR headset. You can see: 1) the overlaid robot model; 2) objects the robot can manipulate; and 3) selectable actions for the wearer, e.g., “clean” up the teddy bear. Click here for the corresponding video!
In line with my ambition to advance the capabilities of assistive robots, my colleague and I developed a novel system that combined an AR headset with a robotic wheelchair [2]. The resulting platform was a first of its kind and I hope to see many more examples of similar assistive robots in the near future. Check out the video below for details.
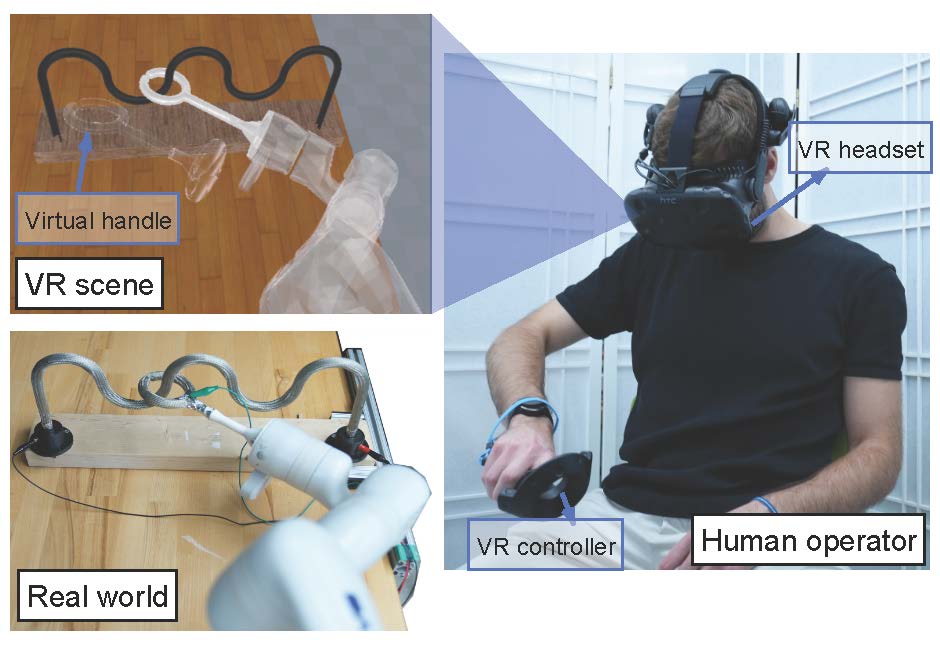
VR headsets also fall within the extended reality spectrum and are useful in gaming, remote teleoperation, and training scenarios. On the right, my colleagues and I designed a physical replica of the buzz wire game to explore how people perform when completing the task by teleoperating a robot in VR.
References
[1] M. Zolotas and Y. Demiris, “Transparent Intent for Explainable Shared Control in Assistive Robotics”, International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020.
[2] M. Zolotas, J. Elsdon and Y. Demiris, “Head-Mounted Augmented Reality for Explainable Robotic Wheelchair Assistance”, IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2018.
